How Accurate Are GPS Speedometers?
In a world where technology continues to evolve at a lightning pace, GPS speedometers have emerged as a reliable alternative to traditional mechanical devices. These devices harness the power of satellite technology to provide real-time speed readings. But how accurate are they, especially when compared to their traditional counterparts? Let’s take a comprehensive look.
1. The Science of GPS Technology
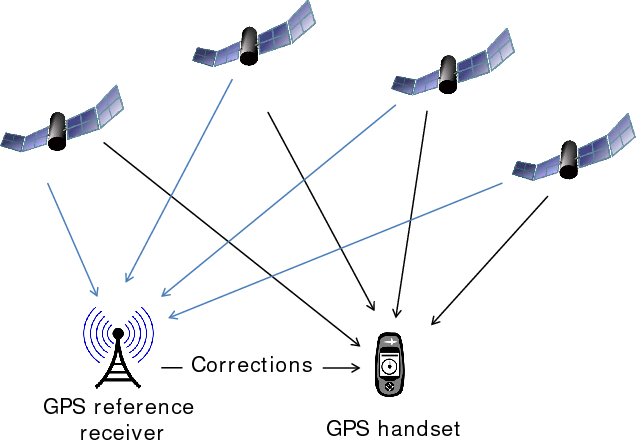
Before we delve into the accuracy of GPS speedometers, it's crucial to understand how GPS technology works. The Global Positioning System (GPS) is a network of about 30 satellites orbiting the Earth. These satellites transmit signals to GPS receivers, like the ones found in your smartphone or car, to triangulate their exact position on the Earth's surface. When determining speed, GPS systems calculate the change in positional data over time. Given the satellite-based nature of this calculation, it's less susceptible to many of the errors that can affect traditional speedometers, such as tire wear or mechanical malfunctions.
2. Factors That Influence GPS Accuracy
Though GPS technology is inherently accurate, several factors can influence the precision of a GPS speedometer:- Satellite Visibility: Buildings, trees, tunnels, or even atmospheric conditions can obstruct satellite signals. The more satellites a GPS device can connect with, the more accurate its readings.
- Device Quality: Not all GPS receivers are created equal. High-end devices generally have better antennas and more advanced software, allowing for greater accuracy.
- Update Frequency: The frequency with which a device refreshes its GPS data can affect accuracy. Devices that update more frequently can offer more accurate speed readings, especially during rapid acceleration or deceleration.
3. Comparing to Traditional Speedometers
Traditional speedometers measure speed by counting the number of rotations of a vehicle's wheel or driveshaft. While they can be highly accurate when calibrated correctly and maintained, they can also be influenced by factors like tire size, wear and tear, and mechanical issues. In general, a well-maintained GPS speedometer can offer accuracy within a few percentages of the actual speed. In contrast, traditional speedometers might deviate by as much as 5-10%, especially if not regularly serviced or if the vehicle is using non-standard tire sizes.
